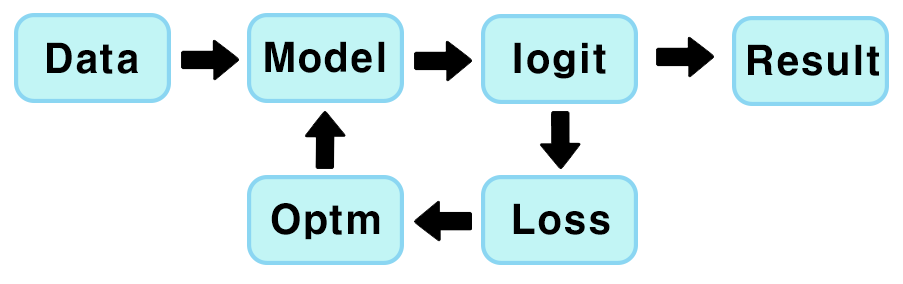
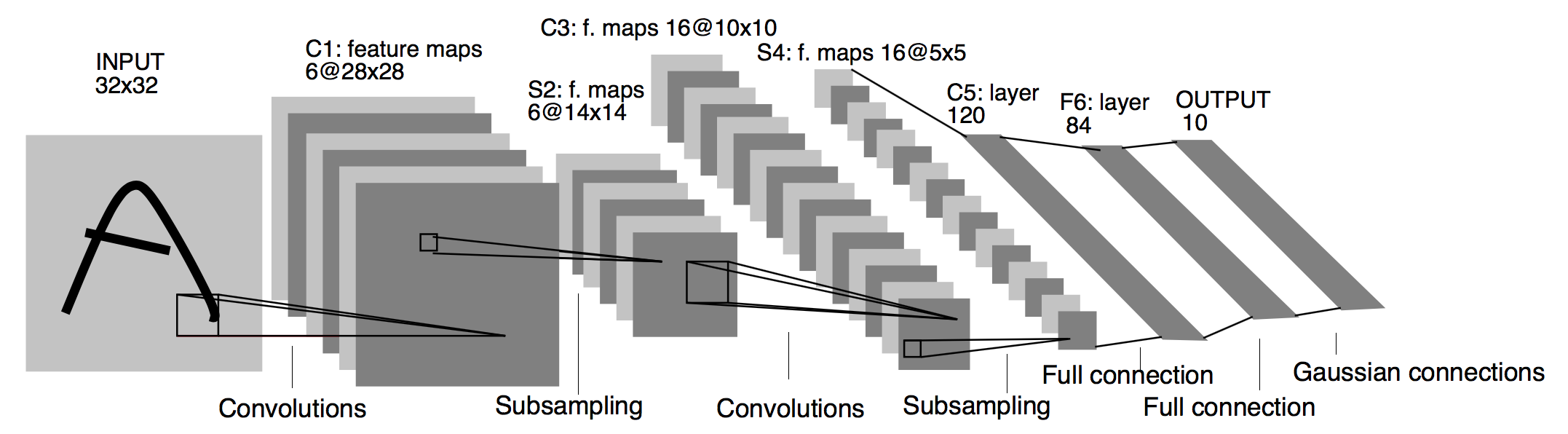
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| inputs = layers.Input((28, 28, 1))
net = layers.Conv2D(32, (3, 3), padding='SAME')(inputs)
net = layers.Activation('relu')(net)
net = layers.Conv2D(32, (3, 3), padding='SAME')(net)
net = layers.Activation('relu')(net)
net = layers.MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(2, 2))(net)
net = layers.Dropout(0.25)(net)
net = layers.Conv2D(64, (3, 3), padding='SAME')(net)
net = layers.Activation('relu')(net)
net = layers.Conv2D(64, (3, 3), padding='SAME')(net)
net = layers.Activation('relu')(net)
net = layers.MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(2, 2))(net)
net = layers.Dropout(0.25)(net)
net = layers.Flatten()(net)
net = layers.Dense(512)(net)
net = layers.Activation('relu')(net)
net = layers.Dropout(0.5)(net)
net = layers.Dense(10)(net)
net = layers.Activation('softmax')(net)
model = tf.keras.Model(inputs=inputs, outputs=net, name='Basic_CNN')
|